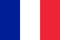
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland caused by various infections. It usually develops in an acute form and is accompanied by an increase in temperature up to 37–38⁰ C, pain in the perineum, and problems with urination.
Untreated acute prostatitis becomes chronic and this is the most common. In this case, the symptoms are less pronounced (pain in the lower abdomen, when urinating, sexual dysfunction, general weakness) or are completely absent. However, the consequences can be very serious. The inflammatory process is directly related to potency problems and is manifested by a decrease in libido, loss of orgasm.
A missed infection greatly increases the risk of developing complications. In particular, it is diseases such as:
- pyelonephritis;
- cystitis;
- prostate abscess;
- Brown planthoppers;
- dry.
Such consequences can be avoided if you consult a doctor in time. Take care of your health now - and in return you will enjoy excellent health, psychological well-being and enhanced self-esteem, quality of sexual relationships.
Causes of prostatitis
This question is relevant not only because many men are facing this problem, but also because most cannot understand where they got this disease from.
Causes of prostatitis in men:
- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Urethritis diseases caused by conditionally pathogenic flora.
- Sexual arrhythmia is an irregular, unbalanced sex life.
- Sedentary is a sedentary lifestyle.
- Urinary stone disease.
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in the body (chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, prostatitis and inflammation of the lower glands, etc. ).
- Abuse of alcohol and spicy foods.
- Constipation.
- Hypothermia.
- Pathology of the lumbar spine and spinal cord - due to a violation of the transparency and nutritive properties of the prostate gland.
Why does prostatitis occur with an STI infection? Genitourinary pathogens, particularly gonococcal, trichomonas, chlamydia, ureaplasma, and mycoplasma, primarily affect the urethra in men, causing venereal urethritis. But, like any living microorganisms, these infections actively multiply under favorable conditions for them, that is, the mucous membrane of the urethra and prostatic ducts.
Of course, if the patient visits a urologist or specialist in time, passes tests for STDs, detects the presence of a sexual infection and cures it, then there will be no excuses. What for the occurrence of prostatitis. Everything will end with the recovery of the anterior urethritis stage. But with a progressive form of the disease, with a formal approach to treating sexually transmitted diseases, when they are tried to cure just by taking broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of tablets and the result is noOnce cured, bacteria enter the posterior urethra. and prostate gland, causing inflammation, i. e. prostatitis, and is often primary-chronic. In this case, it is very easy to avoid developing prostatitis, everything depends entirely on the patient himself.
All you need is:
- Seek immediate medical attention at the first sign of urethral discomfort
- Pass urologist-recommended tests for STIs
- Comprehensive treatment of identified sexually transmitted infections
- Perform control tests after treatment to determine the presence of venereal infections not only in the urethra but also in the prostatic discharge.
- And it's best to go for in-clinic prophylaxis after having normal sex even before symptoms of STDs start and protect yourself and your loved ones from STIs. sex in general and the cause of prostatitis in particular
Symptoms of Prostatitis
How to recognize or suspect prostatitis for an ordinary person, because its symptoms are very similar to many diseases of the genitourinary system and even other organs? What are the symptoms of prostatitis? What are its first signs, and how do they behave with the progression of the disease. We will talk about this in this article.
What other conditions can be confused with prostatitis:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STDs) are the most common situation when a man visits a sexologist after a sexual relationship thinking he has an STI. And in fact, the prostate was inflamed.
- Urolithiasis can cause similar symptoms, but at the same time, it can itself cause an inflammatory process in the prostate gland.
- Cystitis is rare in men, but the symptoms are very similar to prostatitis.
- Pyelonephritis - pyelonephritis has some similarities in symptoms with prostatitis.
- Diseases of the scrotum (epididymitis, orchitis, varicocele) - heaviness and pain in the scrotum can cause these diseases, including prostatitis.
- Diabetes mellitus - the patient notes an increase in urination, as in prostate diseases, but there is no slow flow and the urine output remains normal or even increased.
- Other diseases of the prostate: cancer and adenomas (benign hyperplasia) of the prostate gland.
- Urethritis.
- Diseases of the anus - rectum, hemorrhoids, tumors.
- Diseases of the spine.
For an accurate diagnosis, a urologist not only needs to know the symptoms of prostatitis very well, but also be able to accurately order other diagnostic tests and studies, as well as be able to make a complete assessment. their results.
So consider these signs or symptoms of prostatitis:
Group 1 is pain syndrome. That is, pain occurs in the perineum, in the groin, lower abdomen, scrotum, penis, rectum, sacrum, coccyx, inner thigh. It can be just a painful, pulling, pressing sensation or rather a sharp, stabbing, intense pain. Sometimes a man simply complains of some discomfort in these areas, both when urinating and outside of it. Usually, the pain increases with prolonged sitting in a chair or in a car.
In chronic prostatitis, pain may decrease after intercourse. If there is strong inflammation in the prostate or large calcifications (stones) have formed in the gland, pain during ejaculation may be present.
Group 2 symptoms - urinary disorders. There is an increase in urination, first at night, then throughout the day. Urine flow becomes sluggish, partial volume decreases, urine clarity decreases, blood may appear. When the prostate is severely swollen or the gland is fibrous around the urethra, you may find it difficult to empty your bladder. A man must strain, wait a while to pee.
Group 3 - violation of sexual function. In the early stages of prostatitis, there is some increase in libido, arousal and premature ejaculation. Further down is due to decreased production of sex hormones leading to decreased libido, decreased ability to have an erection. A man is either unable to have intercourse, or, having begun, is unable to end it. But, even with ejaculation, orgasm is insidious or barely felt. If an erection or ejaculation is accompanied by pain, it means that the man himself refuses new contacts, which adversely affects later sexual function due to prolonged abstinence. And this also leads to the progression of congestive prostatitis. A vicious circle emerges.
Group 4 - these are general symptoms. There may be an increase in body temperature, fatigue, weakness, irritability, which is associated with the presence of inflammatory processes and hormonal imbalances, and failures in the sex life. . Some patients have increased sweating (profuse sweating) in the groin area, red foreskin of the penis.
With a sufficiently pronounced inflammatory process in the prostate gland from the urethra, there may be a mucus or purulent discharge.
The clinical picture of each patient with prostatitis is individual. Not all groups of symptoms are necessarily present, and not all of them may be evident. With a chronic process in the prostate gland, a clear clinic and minor symptoms are observed, but this does not make it the least dangerous for a man's health.
Therefore, if you notice any symptoms of prostatitis from above, urgently make an appointment with a urologist. Do not delay in contacting the doctor, because even if the discomfort has passed, this does not mean that the inflammatory process has stopped. It only moves to a latent stage that will gradually degrade health and destroy the prostate gland.
The best option is a preventive visit every six months by a urologist with a diagnosis of palpation of the prostate, microscopic prostatoscopy, ultrasound, and a PSA blood test. So you protect yourself from the negative consequences of not only progressive chronic prostatitis, but also adenomas and prostate cancer.
Prostatitis treatment
Modern treatments for prostatitis include the following:
- drug therapy (prescribe antiviral and antifungal drugs);
- maintenance treatment (prescribing immunostimulating drugs, taking dietary supplements);
- urinary massage (massage of the prostate);
- LOD-therapy (a method that uses low pressure to restore potency);
- a special set of physical exercises for relaxation;
- Doctor's recommendations in matters of nutrition, lifestyle, sex.
In treatment, I use the best methods of leading medical centers and my own development should give excellent results.
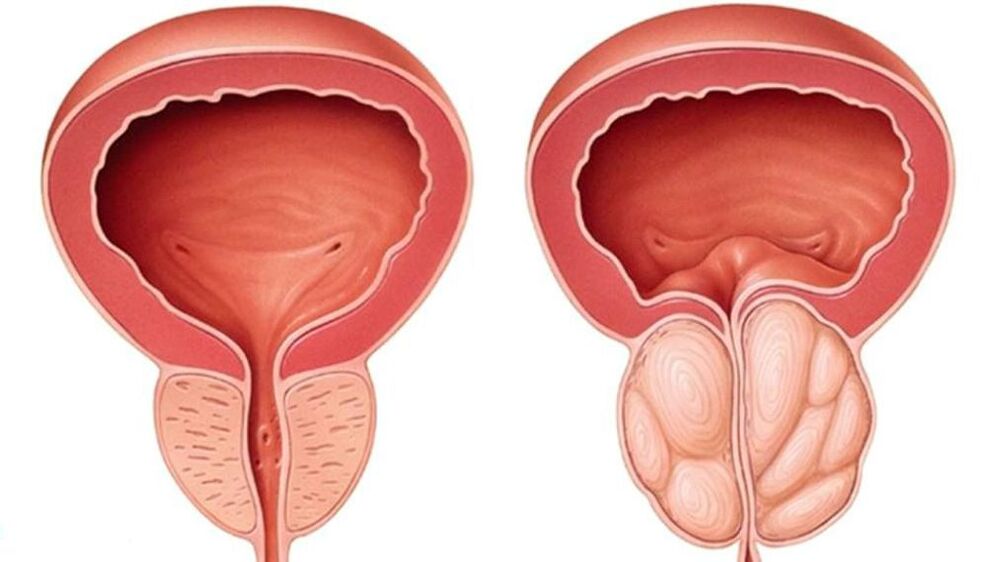
Congestive (congestive) prostatitis
Treatment of congestive prostatitis presents certain difficulties, as the cause of this type of prostatitis is the lifestyle and sexual activities of men. Accordingly, only the patient himself, not the doctor, can directly influence these processes. But even in such a difficult situation, the patient can be helped. For the treatment of congestive or congestive prostatitis, a special complex therapy has been developed that allows you to eliminate the effect of blood stagnation in the prostatic plexus and the secretion of the prostate gland. prostate in its ducts and acini.
Treatment of congestive prostatitis
After a preliminary diagnosis, including:
- Analysis of prostate secretions for microscopy, STIs, cultures
- Blood test for PSA
- General urine and blood tests
- Blood chemistry
- Ultrasound of the prostate gland, its venous plexus
- kidney ultrasound
The diagnosis of chronic congestive prostatitis is established, a complex of drug therapy and necessary procedures is determined, which includes:
- Rectal prostatic massage is necessary to remove the leukocyte plugs, mucus, and congestive inflammatory secretions of the prostate gland from the ducts. This is the main treatment procedure that also improves blood flow in the prostate gland, acting as a factor in the fight against blood stasis.
The massage is performed by a urologist. Session duration from 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Quantity from 10 pieces per lock. The cost is 600 rubles.
Even if the patient does not have the opportunity to complete a full course of congestive prostatitis, at least 10 massage sessions must be attended. Drugs alone do not provide the desired effect in the treatment of prostate obstruction.
- Prostatitis is a very good and effective procedure in the treatment of congestive prostatitis. With the help of a special device that generates vibrations, heat and magnetic fields, the blood supply to the gland is improved, the attachment of leukocytes to the wall of the prostate duct is weakened, creating favorable conditions. beneficial for their removal during subsequent finger massage. It is usually done right before a massage session.
- Magnetic laser therapy improves blood flow and properties of the gland, removes inflammatory products from it, reduces swelling. Many patients feel its effects within the first days of treatment in the form of pain relief and a feeling of tightness in the prostate area.
This method of treating congestive prostatitis has been around for a long time and has been successfully applied for many years, constantly being updated, including modern new methods and approaches. Chronic prostatitis can and should be treated, providing long-term remission and significantly improving the quality of life of a modern man.
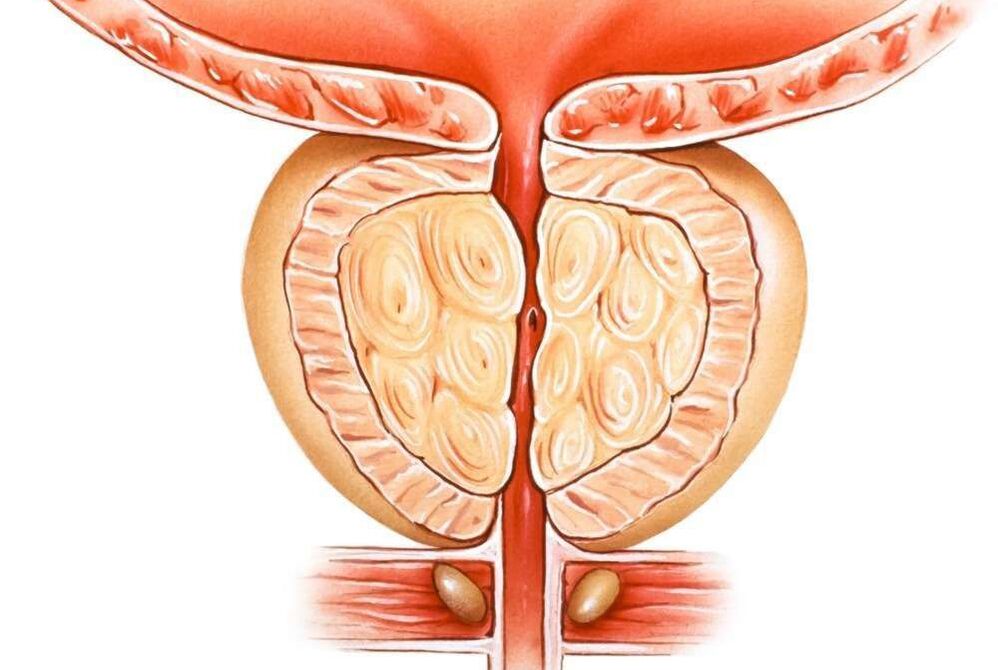
BPH
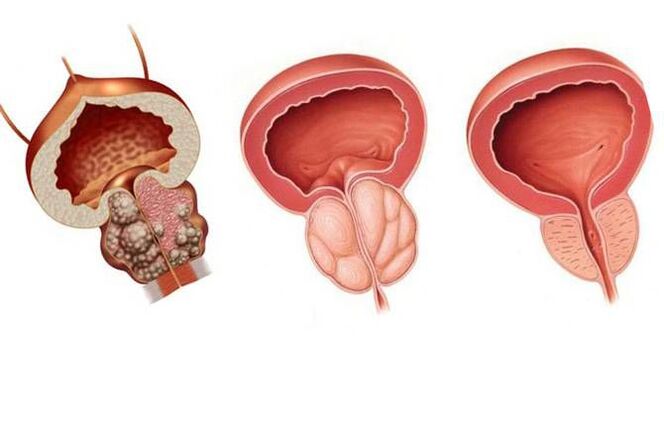
Prostate cancer, or now commonly known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a chronic disease that mainly occurs in older men, at least after the age of 50. After 70 years, more than 50% of men have had complications of this disease. Although there are cases of its earlier development.
Prostate tumors are accompanied by growth of glandular and stromal (connective) tissue. As a result, nodules form according to the thickness of the gland, which, when they reach a large size, begin to compress the surrounding tissues - the bladder, urethra, rectum and sometimes even the ureters, disrupting functioning. normal functioning of these organs.
Reasons for the development of prostate tumors
The growth of prostate tumors is associated with hormonal imbalances in older men, i. e. a manifestation of "male menopause". Over the years, there has been a decrease in the production of the main male hormone testosterone by the testes and an increase in the levels of the female hormone estradiol (especially in men with high body fat mass). A direct negative effect of female hormones on the prostate gland has been demonstrated, as well as increased production of dihydrotestosterone in prostate cells, causing active tissue growth and the development of glandular hyperplasia. Benign prostate, i. e. adenoma.
Reasons for the development and progression of BPH can also include:
- hypodynamia - sedentary lifestyle
- alcohol abuse and smoking
- fatty, cholesterol-rich, spicy, spicy food
- low sexual activity
In principle, chronic prostatitis is not the cause of prostatic hyperplasia, but with a concomitant course it contributes to more obvious symptoms and the rapid development of complications. symptoms of prostate hyperplasia.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Symptoms of prostate cancer depend on the stage of the disease, its decompensation, the development of complications, and the direction of tumor growth.
- First of all, symptoms such as difficulty urinating, slow urination, frequent urination for 15-20 times a day, nocturia - nocturia.
- Then, when the bladder muscle is weak, pain in the lower abdomen, feeling that the bladder is not completely empty, urine is excreted in parts, drop by drop, you have to stretch your abdominal muscles. It ends with the complete loss of the propulsion - the muscles of the bladder that expel urine.
- When combined with chronic prostatitis, there is pain in the perineum, rectum, fever, mucus and pus discharge from the urethra.
- The urine is discolored, cloudy, and may contain drops of blood.
- Reduced sexual function.
- With the growth of the prostate tumor towards the triangle of the bladder formed by the orifices of the ureters and the urethra, obstruction of the ureters and violation of urine outflow from the kidneys, ending with a faster development of the diseasechronic kidney disease. failure and urolithiasis.
The main complications of prostate cancer:
- Urgent urinary retention - urgent bladder catheterization is required.
- As a result of urine stagnation, urolithiasis and inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis), bladder (cystitis) and urethra develop.
- Presence of blood in the urine.
Chronic kidney failure is a serious complication that can lead to death.
Prostate tumor treatment
Clinics that treat prostate tumors without surgery, i. e. drug treatment, are most effective for stage 1 and sometimes 2 prostate fibroids.
Prostatectomy is performed with decompensation, a large mass of prostate tumor that grows toward the triangle of the bladder. It has many different types:
- starting with an open thyroidectomy - removal of the tumor through the bladder
- ended with minimally invasive method, when urethral catheterization with the aid of electrocautery, radio wave and laser techniques, the urethra is freed from adenoma or areas of prostate hyperplasia are removedcompletely.
In order not to get it, the first time you visit a urologist, you will immediately be offered surgery for a prostate tumor, you need to undergo an annual prostate exam, ultrasound and screening tests. PSA blood test.
Prostate massage
One of the most common and very effective therapeutic and diagnostic procedures in urology and biology is prostate (prostate) massage. This operation has been used by urologists for a long time and is familiar to most patients with prostate, seminal vesicles and STIs.
Why is prostate massage used?
Prostate massage can be used in two cases:
For diagnostic purposes for:
- Take prostate secretions for microscopic analysis
- Determination of the presence of sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmas, mycoplasmas, gonorrhea, etc. ) in the prostate by PCR, PIF and other methods
- Obtaining culture material to determine microbiome and antibiotic sensitivity
- Collecting subjective data on the tenderness, density, and size of the gland - the so-called diagnostic palpation of the prostate
For therapeutic purposes:
- to free the ducts of the gland from the white blood cells and mucus plugs
- to improve blood circulation in the prostate, which leads to better penetration of the drug into its tissues and the elimination of blockages
When to massage the prostate?
Prostate massage is indicated for many men's health problems, for example:
- chronic bacterial and bacterial prostatitis
- chronic seminal vesicles - massage of the prostate and seminal vesicles
- chronic and sluggish urethritis
- prostatitis due to genital infection
- Erectile dysfunction and infertility related to prostate diseases
- for the purpose of prevention in the treatment of end-stage STDs
Prostate massage should not be performed in case of acute purulent inflammation of the genitals!
How is prostate massage performed?
There are several classic prostate massage positions.
The most common is the knee-elbow position, when the patient stands in a chair, his knees and arms are bent at the elbow joint, bent at the waist.
In diseases of the spine, old age, large body weight, can lie on the left side, knees bent, brought to the abdomen.
When massaging the seminal vesicles, the patient stands with his feet on a chair, with his back to the doctor, and in a semi-squat position.
During prostate massage, the urologist's index finger is inserted into the patient's rectum and begins to alternately massage the right and left lobes of the prostate gland, ending with the intervertebral groove (the isthmus). ). During this operation, which lasts from 30 seconds to 2 minutes, the doctor receives information about the pain of the gland, its size, consistency, surface, severity, and possible bile collection. of the prostate gland for analysis.
During prostate massage, there may be some discomfort, the need to urinate, a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen, penis. When there is severe pain, the massage will stop.
It is very important that the procedure is performed by a qualified urologist or specialist so as not to harm the man and not damage the prostate gland.
Vibrations of the prostate

Vibration of the prostate - the use of vibration, magnetic fields and heating in the treatment of chronic prostatitis. This type of physical therapy improves the blood flow and nutrition of prostate tissue. The vibrator helps to remove white blood cells from the ducts of the gland. With prostatitis - one of the alternatives to finger massage. The duration of the lesson is from 10 to 20 minutes.
Prostatitis prevention
Prostatitis prevention includes avoiding factors that predispose to prostatitis, as well as:
- Try not to freeze for a long time, if you have to stay in a cold room or outside for a long time, pay attention to appropriate clothing.
- For constipation, take a laxative and don't beat yourself up.
- If you have a sedentary job, give yourself a "fitness break" every hour (or at least just get up and walk around).
- Try to have a regular sex life, as this perfectly fits into one's normal lifestyle and allows you to avoid many problems, not just prostatitis.
- Try to eat well and enough, keep an active lifestyle, don't get sick and finally, think about your health from time to time.
And don't forget to visit your urologist regularly.